When preparing for a networks-related job, you should know and understand the arp interview questions. ARP is a very important concept and protocol related to networks engineer interview. Questions regarding address resolution protocol can be tricky, but if you know what to expect, you’ll have a much easier time acing the interview.
ARP Interview Questions
In this blog post, we’ll look at some of the most common interview questions related to ARP protocol and provide tips on answering them. Here are some of the most anticipated interview questions on ARP Address Resolution Protocol:
What is ARP?
Address Resolution Protocol maps the IP address to a machine’s MAC address, and networks determine that. ARC works at layer 2 of the OSI model, and all the communications between two devices at the data-link layer are done through the physical address. So ARC basically replace the IP communication by MAC address by building a MAC table.
How does ARP work?
A host sends an ARP request datagram, which contains the IP address of another host, to its local network. The local network broadcasts this message to all hosts on the local network. The host receives the message with the specified IP address, and that host responds with an ARP reply datagram containing its physical address. The original host can now map the IP address to a physical address and use it to send datagrams.
- If the host’s IP address resolved, the ARP module will send an ARP reply packet containing its Ethernet MAC address.
- If the IP address being resolved is for this host, then the ARP module updates the ARP cache with the source Ethernet MAC addresses to the source IP address mapping in the ARP request package. It is overwritten if the entry is already in the cache. It is overwritten if it isn’t.
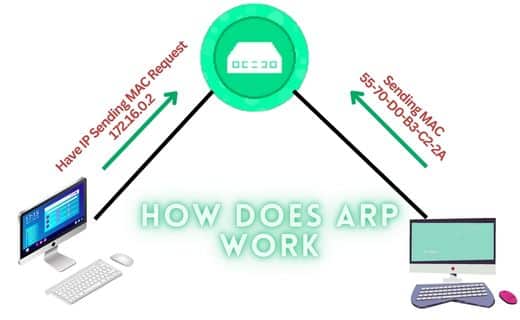
- The ARP module will discard the ARP request packet if the resolved IP address does not belong to this host.
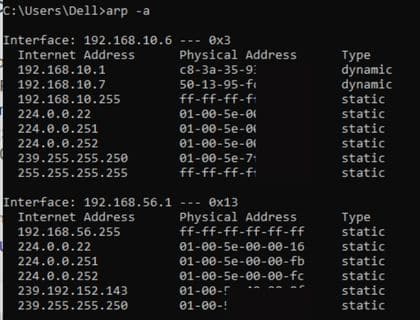
What is the arp cache?
The arp cache is a table that stores mappings of IP address to physical addresses. The arp cache is used by hosts to quickly resolve IP addresses to physical addresses without sending an ARP request datagram.
What is gratuitous arp?
Gratuitous arp is a type of arp datagram used to update the arp cache of other hosts on the local network. Gratuitous arp datagrams are often used when a host’s IP address or physical address has changed.
What happens when an arp entry expires?
When an arp entry expires, the host will remove the mapping from the arp cache and will have to send an ARP request datagram the next time it needs to resolve the IP address.
What is inverse ARP?
Inverse Address Resolution Protocol (Inverse ARP or InARP) is utilized to get the network layer addresses (for instance, IP addresses) of other nodes based on Data Link Layer (Layer 2) addresses. Because ARP converts layer-3 addresses into layers-2 addresses, InARP can be described as the reverse.
What is reverse ARP?
Reverse arp (RARP) is a protocol that allows a host to obtain its own IP address from a host when its MAC address is known. RARP is used when a host does not have a static IP address and needs to obtain one from a server.
Which OSI layer ARP belongs to?
ARP belongs to the data link layer (Layer 2).
What is the arp command?
The arp command is a utility that can be used to view and modify the arp cache. The arp command is available on most Unix-like operating systems.
Explain the ARP message Header format and its Size.
ARP header is 28 bytes and has the following 9 fields:
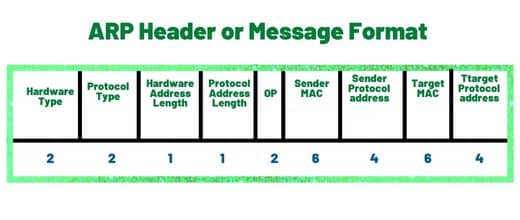
- Hardware Type of 2 Bytes
- Protocol Type (2 Bytes)
- Hardware Address Lenght (1 Byte)
- Protocol Address (1 Byte)
- OPCode (2 Bytes)
- Sender MAC (6 Bytes)
- Sender Protocol Address (4 Bytes)
- Target MAC (6 Bytes)
- Target Protocol Address(4 Bytes)
What are the four types of ARP?
The format is comprised of four different types of proxy arp:
- Gratuitous arp
- Proxy ARP
- Inverse ARP
- Reverse arp
what is ARP Prob?
An ARP probe within IPv4 can be described as an ARP query made using an SHA set to zeros, and the SPA assigned to the targeted IPv4 address. A host can transmit an ARP probe to identify and address conflicts.
A switch may also use an ARP probe to determine a host’s location with a given IPv4 address.
what is arp stuffing
ARP stuffing allows you to establish a network connection with other devices, such as embedded systems like networked cameras or power distribution devices.
These devices usually can turn off this feature after the device has typically been functioning since the ability to disable this process can make it vulnerable to attacks.
What Will Happen If A New Arp Request Packet Is Received, But The Mac Address To Ip Address Is Already Present In The Arp Cache? If a brand new Arp Request packet arrives, however, the mac address for the IP address is already within the cache of arp Arp Cache will get updated to reflect new information.
Does ARP use a switch?
The switch keeps an ARP table comprising the mapped IP addresses and additional MAC addresses. When a request needs to be directed to a specific source, the device searches at its IP address within its ARP table and determines the address for the device to be routed. The ARP table contains both dynamic and static addresses.
Does ARP work across routers?
The ARP protocol is an underlying layer two protocol and its primary function is to convert the MAC address to the IP address and reverse. The router is a layer three device, and all communication happens in the context of the IP address. It can simply put the packet onto the network interface so that it can reach the router that is in another.
How is the ARP table created?
ARP tables are typically generated automatically by an ARP request, and the reply process discussed previously. There are occasions where manual modifications to the table need to be done. Be sure to understand how these changes impact the network and ensure that you follow the proper procedure to remove or add manually-created entries. These might differ between different devices. ARP entries can be modified by using a CLI, or the device’s graphic user interface. Each procedure may differ, but generally speaking, the steps and details required to edit entries are identical.
Who maintains ARP table?
Every host in an internet network has an arp table of its own. Arp tables is used to record IP address mappings in physical addresses.
Network nodes use ARP in IPv4 networking to keep track of peer network nodes. ARP associate the Layer 3 IP addresses with Layer 2 MAC addresses of neighboring peer networks. The system supports an ARP table that contains dynamic, cached entries. You can also add static entries as needed.
What is the arp table used for?
It is the arp table that stores IP address mappings to physical addresses. The host utilizes the arp table to convert IP addresses to physical addresses.
What is the Difference between ARP and MAC tables?
The ARP tables build with the IP addresses of the devices and the MAC addresses. It is constructed by analyzing responses to ARP requests and it is also known as the MAC address table, often called “The MAC Forwarding Table,” and a Forwarding Database (FDB), which provides information regarding the port on which a specific device is connected. When the network switch makes choices regarding the usage of packets that impact the MAC table, the MAC table will determine what can be forwarded by which port.
Conclusion:
If you are looking for a job in the network field, it is essential to know about ARP interview questions. Most companies will ask questions about this topic, so you must be prepared. We’ve provided a list of some of the most frequently asked questions to help you prepare better to go into your interview. We hope you find these useful and useful to you. We wish you the best of luck in finding a job!