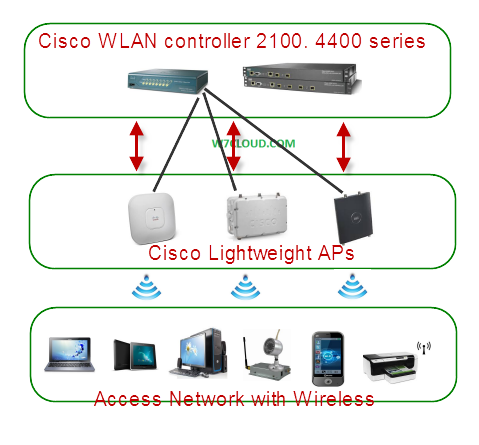
The main standard for wireless LAN is the 802.11. WLAN applications include inside-building access, LAN extension, outside building-to building communications, public access, and small office/home office communications. Some of the famous standards that are used in wireless communication are:
802.11 Wireless Standard:
802.11 is for wireless local area network standard and the original 802.11 standard was introduced in 1997 by IEEE.
- It uses two different types of RF technologies that are FHSS (Frequency-hopping spread spectrum) and DSSS (direct-sequence spread spectrum).
- FHSS and DSSS operating on in 1 Mbps or 2Mbps and 802.11 operate in 2.5 GHz frequency range.
- 802.11 family use half duplex modulation.
- 802.11b and 802.11g are most famous standard used in wireless communication.
802.11b Wireless Standard:
The 802.11b standard was introduced in 1999 by IEEE.
- It uses the DSSS (direct-sequence spread spectrum) at the frequency range 2.4 GHz.
- 802.11b use the bracker-11 and CCK encoding scheme. Modulation types that are used in 802.11b are DBPSK and DQPSK.
- 802.11b has the data rates from 1Mbps to 11Mbps, for the different data rates (1, 2, 5.5, 11Mbps) you have different modulation techniques.
- In 802.11b you have three non overlapping channels which are 1, 6 and 11.
802.11g Wireless Standard:
802.11g was introduced in 2003 and also compatible with 802.11b.
- RF modulation technologies that are used by 802.11g are DSSS and OFDM.
- 802.11g operate in 2.4 GHz spectrum.
- In 802.11g you have three non overlapping cannels 1, 6, 11.
802.11a
This standard was come in 1999.
- 802.11a use OFDM.
- 802.11a provides a maximum 54-Mbps data rate.
- 802.11a operates in 5.0 GHz frequency.
- 802.11a is incompatible with 802.11 b and g.
- 802.11a is not mainly used standard as compared to 802.11b and 802.11g.
- 802.11a has the data rate from 6-54 Mbps.
- The data rate is reduced to 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 then 6 Mbit/s if required. 802.11a originally had 12/13 non-overlapping channels
802.11n Wireless Standard
- The IEEE 802.11n standard was ratified in 2009.
- It added multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antennas and expected maximum data rate up to 600 Mbps using four spatial streams, each with a 40-MHz width.
- In addition to DSSS, it uses orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) as a digital carrier modulation method. IEEE 802.11n uses both the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz bands.
How to increase wifi signals of wifi router.