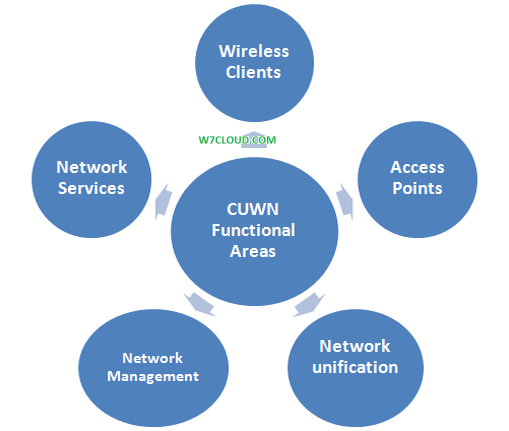
Cisco Unified Wireless network is methodology for designing the wireless network and it have the following components:
- Wireless Clients
- Access points
- Network management
- Network Unification
- Network Services
Wireless Clients: Wireless Clients includes the laptops, PC, Mobiles Phone, PDAs and IP phones. These all end devices are the part of access network.
Access points: AP provides the wireless access to network. You need to place the access point at the best place to avoid the interference with other access point and to provide the best access to your wireless clients.
Network management
Network management related to wireless control system (WCS), WCS is the central management tool for design and monitoring of our wireless network.
Network Unification: According to Network Unification our WLAN should be able to support the wireless application by offering the security policies, unified services, IPS and manage of radio frequency.
Network services are also referring to mobility services and this includes the things like guess access, location services and threat detection services.
LWAPP (light weights access point protocol) Overview
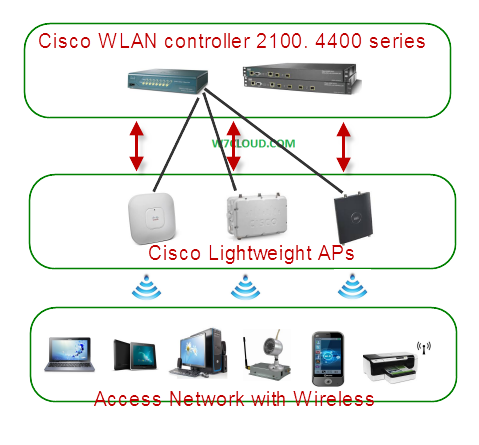
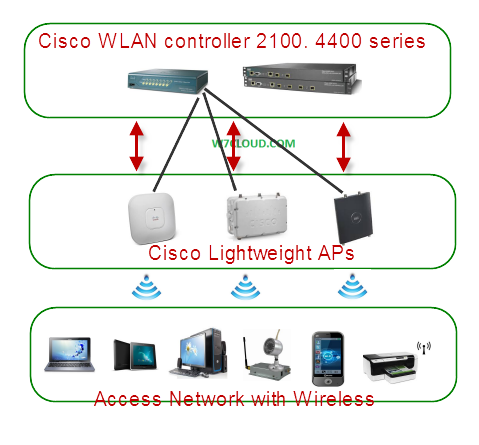
LWAPP is the standard for WLAN controllers and LWAPP operate at layer-2 and at layer-3. Wireless LAN controllers are very important part of Cisco wireless network and wireless LAN controller is used in combination with the Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) to manage the multiple light weight APs. The WLAN controller automatically handles the configuration of anywhere from 6 to 6000 wireless access-points, depending on the model. The concept of LWAPP is we are moving the intelligence away from access point and sharing it with some type of WLAN controller. WLAN controller can handle the intelligence and can implement different policies, control messaging, authentication and operations between the access point and WLAN controller.
For better understanding of LWAPP please consider the following diagram where we have light weight access points which include indoor or outdoor access points those are handled with the Cisco WLAN controller (Cisco 2100 series and 4400 series WLAN controllers). LWAPP is use for management and control between these lightweight APs and wireless controllers. With split MAC operation data messages are split up in the wireless network, wireless access point communicate with wireless controller using control messages over the wired back bone network and then LWAPP data messages are forwarded to wireless clients. Wireless LAN controller can manage and handle the multiple access points at a time.
LWAPP Discovery of WLC
When LWAPs are placed on the network, they first perform DHCP discovery to obtain anIP address. Then Layer 3 LWAPP discovery is attempted. If there is no WLC response, theAP reboots and repeats this process. The Layer 3 LWAPP discovery algorithm is as follows:
- The AP sends a Layer 3 LWAPP discovery request.
- All WLCs that receive the discovery request reply with a unicast LWAPP discoveryresponse message.
- The AP compiles a list of WLCs.
- The AP selects a WLC based on certain criteria.
- The AP validates the selected WLC and sends an LWAPP join response. An encryptionkey is selected, and future messages are encrypted.
At the layer-3 we have the LWAPP tunnels which are used between the wireless controller and access points. Messages from wireless controller are send to access point using the UDP port 12223 for control and port 12222 for data message.
LWAPP Modes:
LWAPP can operate in six different modes, for CCDA exam these modes are very important.
- Local mode
- REAP Mode
- Monitor mode
- Rogue Detector Mode
- Sniffer mode
- Bridge Mode
Local mode:this is the default mode of operation in LWAPP access points. Every 180s the access point spin 60ms on cannel, during this 60ms time period the access point perform the noise measurements, interference and scan for intrusion detection system events.
REAP Mode:Remote edge access point mode allow the LWAPP to reside across the WAN link and still be able to communicate with the wireless LAN controller and provide the functionality of regular LWAPP. REAP mode is only supported on Cisco 1030 light weight access points.
Monitor mode: Monitor mode is the special feature of LWAPP, this allow LWAPP enabled access point to exclude themselves from dealing with data traffic between clients.
Rogue Detector Mode: This is used to monitor the rogue access point, rogue detector’s goal is find and to see all the VLAN in the network because rogue access point is connected to any of VLAN in the network. The switch sends the entire rogue MAC address list to rogue detector and then forward it to wireless LAN controller to compare the MAC address of the clients and if the MAC is matched then it mean that client is on the wired.
Sniffer mode: With sniffer mode access point can capture and sniff all the packets and then shadow then to a machine running Sniffer application. You can enable the sniffer mode with the help of airopeek(a third party software).
Bridge Mode: this mode operates on Cisco 1030 and 1500 series access points. You can use the bridge mode for point to point connection and bridge connection between the two access points.
Wireless LAN controller components:
There are the three main components of wireless LAN controllers that are
- Wireless LANs
- Interfaces
- Ports
Wireless LANs is basically your wireless SSID or wireless network name and it is a logical entity. Each wireless LAN interface is assign in the wireless controller and each wireless LAN is configure for RF policies and Qos. Related Article: View Wifi password on Android phone
Interfaces are logical connection to each LAN controller and each interface is configured with an IP address, a default gateway, physical ports, VLAN tagging and a DHCP server.
Ports are the physical connection to neighboring switch or router and by default each port is a dot1q trunk port. You may have the multiple ports on wireless LAN controller and these port can also be aggregate with link aggregation.
On the wireless LAN controller you have the five types of the interfaces:
- Management interface
- Services port Interface
- AP manager interface
- Dynamic interface
- Virtual interface
Also each wireless LAN controller have different number of AP support, for example Cisco 2100 series support 6 access point, the 4400 series support 100 APs and wireless services module for 6500 series support 300 access points.
| Platform | Number of Supported Access Points |
| Cisco 2100 series WLC
|
25 |
| Cisco WLC for ISRs | 25 |
| Catalyst 3750 Integrated WLC | 50 |
| Cisco 4400 series WLC | 100 |
| Cisco 6500/7600 series WLC module | 300 |
| Cisco 5500 series WLC | 500 |
Roaming and Mobility IN WLAN:
Roaming happens when your wireless client changes their association from one access point to other access point, as a network designer we have to think that how we can scale our network for supporting roaming process. There are two type of wireless roaming that are