Read only domain controller (RODC):
Microsoft introduces a new type of DC in server 2008 that is RODC. The read only domain controller
- Only have the read only copy of directory database,
- Read only active directory have all the objects like user groups, all member groups are there but password are omitted for security reasons. RODC does not store the password of the account.
- Updates are replicated to RODC with read write domain controller. The domain controller that never talk back.
RW–>RODC
- Password caching: All domain user accounts can be cached on the RODC. If you enable password caching on the RODC, it only affects the cache to the local computer and user accounts.
Purpose of RODC | Why RODC
There are some reasons or environment where it is better for you to install read only domain controller.
There are as follow:
- Small branch office:
Suppose you have a small branch office where you don’t have infrastructure to install read write domain control, you have Poor physical security. Therefore it is better here to install RODC.
- Where you have relatively a small number of users
- No IT Staff: RODC is handy where you have IT staff or some inexperience staff.
- Relatively poor network bandwidth to a hub site
Credential caching in RODC:
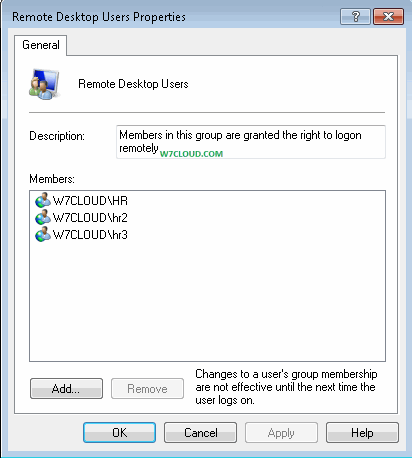
This is for read only domain controller, where domain controller is verifying your credential directly, normally when you log on the RODC it forward login request to read write domain controller. You can select the number of passwords are caching.
Another concept in RODC is administrator role separation which is very useful, could be an account that is using as credential casing you can login on domain using this account when you are disconnected from central office and WAN link is down. For such case you can delegate administrator role to any user you want, that is may not be an administrator but can be login when WAN is down. This user is only admin for RODC not for entire network. You can run updates, you can install drivers and other administrative tasks using this user.